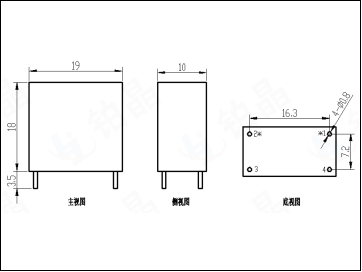
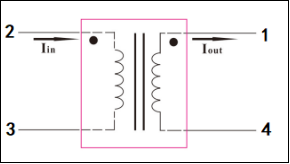
The application principle of the current input voltage transformer is: first, the primary voltage to be converted is converted into a 1-6mA current through a current limiting resistor and input into the primary end of the voltage transformer. The primary and secondary turns of the voltage transformer are equal. A resistor is connected in parallel to the secondary of the transformer, and then the weak current of the secondary is converted into a voltage signal output. The current type voltage transformer can reduce the size of the device as much as possible, which is conducive to the miniaturization of the instrument. However, the current type voltage transformer requires a current limiting resistor, and its stability directly affects the conversion accuracy of the transformer; especially when the measured voltage level is high, it is more important to pay attention to the dissipated power of the current limiting resistor must meet the design requirements, and pay attention to its heat dissipation conditions. At the same time, the secondary load capacity of the transformer is poor, and the general output voltage is not greater than 1V. Excessive output voltage will reduce the dynamic range and linear accuracy of the transformer. In terms of secondary signal processing, a smaller load resistor can be used in combination with a precision rectifier amplifier circuit. It can not only ensure the conversion accuracy, but also ensure the secondary sampling accuracy, but also reduce the dissipated power of the current limiting resistor, which is conducive to reducing costs and improving the reliability of the circuit.
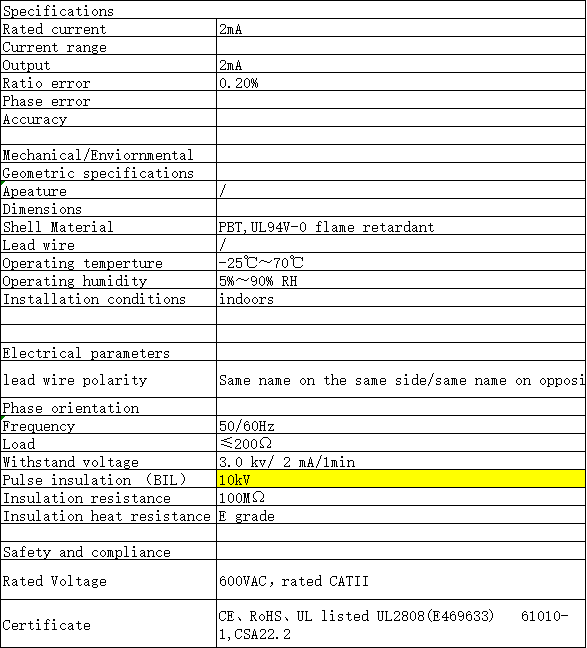
Features:
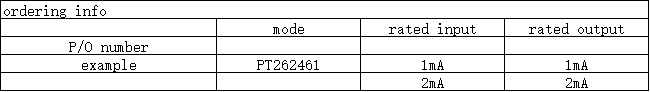
●Accuracy level: 0.1%, 0.2%
●Current input range: 1mA, 2mA
●Output options: 1mA, 2mA
●CE, RoHS, UL listed UL2808

Add:Sanqing Century Wealth Center, Tianchen Road, Lixia District, Jinan City
Email:export@bojingchina.com
Fax:0531-85708558